
Write a C program to declare, initialize and access structures. In this post I will explain how to declare, initialize and access structures in C language. Different ways to initialize a structure variable and how to access structure members.

is a user defined data type. It is a collection of different types combined together to create a new type.
We use struct keyword to declare a structure.
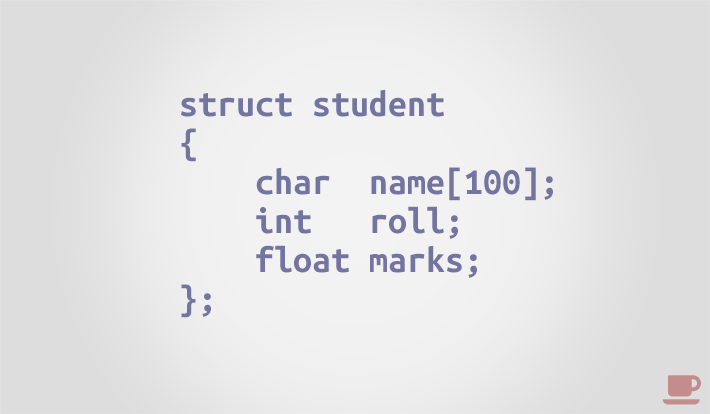
Let us declare a student structure containing three fields i.e. name , roll and marks .
struct student < char name[100]; int roll; float marks; >;C language supports multiple ways to initialize a structure variable. You can use any of the initialization method to initialize your structure.
In C, we initialize or access a structure variable either through dot . or arrow -> operator. This is the most easiest way to initialize or access a structure.
Example:
// Declare structure variable struct student stu1; // Initialize structure members stu1.name = "Pankaj"; stu1.roll = 12; stu1.marks = 79.5f;The above method is easy and straightforward to initialize a structure variable. However, C language also supports value initialization for structure variable. Means, you can initialize a structure to some default value during its variable declaration.
Example:
// Declare and initialize structure variable struct student stu1 = < "Pankaj", 12, 79.5f >;Note: The values for the value initialized structure should match the order in which structure members are declared.
Invalid initialization:
// Declare and initialize structure variable struct student stu1 = < 12, "Pankaj", 79.5f >;The above code will throw compilation error. Since the order of member type in structure is character array, integer finally float. But, we aren’t initializing the structure variable in the same order.
The above approach may suit all needs. In addition, C language supports flexibility to initialize structure members in any order. I know this sounds bit confusing. As, just now I said C will throw error if you try to initialize members in different order of declaration.
This approach is an extension of above. Here, you can specify member name along with the value.
Example:
// Declare and initialize structure variable struct student stu1 = < .roll = 12, .name = "Pankaj", .marks = 79.5f >;Default initialization of a variable considered as good programming practice. However, C doesn’t support any programming construct for default structure initialization. You manually need to initialize all fields to 0 or NULL .
Initializing all fields to NULL is bit cumbersome process. Let’s do a small hack to initialize structure members to default value, on every structure variable declaration.
Example:
// Define macro for default structure initialization #define NEW_STUDENT < "", 0, 0.0f >// Default initialization of structure variable struct student stu1 = NEW_STUDENT;/** * How to declare, initialize and access structures in C language */ #include // Macro for default student structure initialization #define NEW_STUDENT < "", 0, 0.0f >// Student structure type declaration struct student < char name[100]; int roll; float marks; >; int main() < // Declare structure variable with default initialization struct student stu1 = NEW_STUDENT; // Read student details from user printf("Enter student name: "); gets(stu1.name); printf("Enter student roll no: "); scanf("%d", &stu1.roll); printf("Enter student marks: "); scanf("%f", &stu1.marks); // Print student details printf("\n\nStudent details\n"); printf("Name : %s\n", stu1.name); printf("Roll : %d\n", stu1.roll); printf("Marks: %.2f\n", stu1.marks); return 0; >Enter student roll no: 12 Enter student marks: 79.5 Student details Name : Pankaj Prakash Roll : 12 Marks: 79.50